Robot 3D Printing with Cura
Additive manufacturing (or 3D printing) with robots can be accomplished by preparing toolpaths in a slicer such as Ultimaker Cura and converting the generated G-code into robot programs with RoboDK.
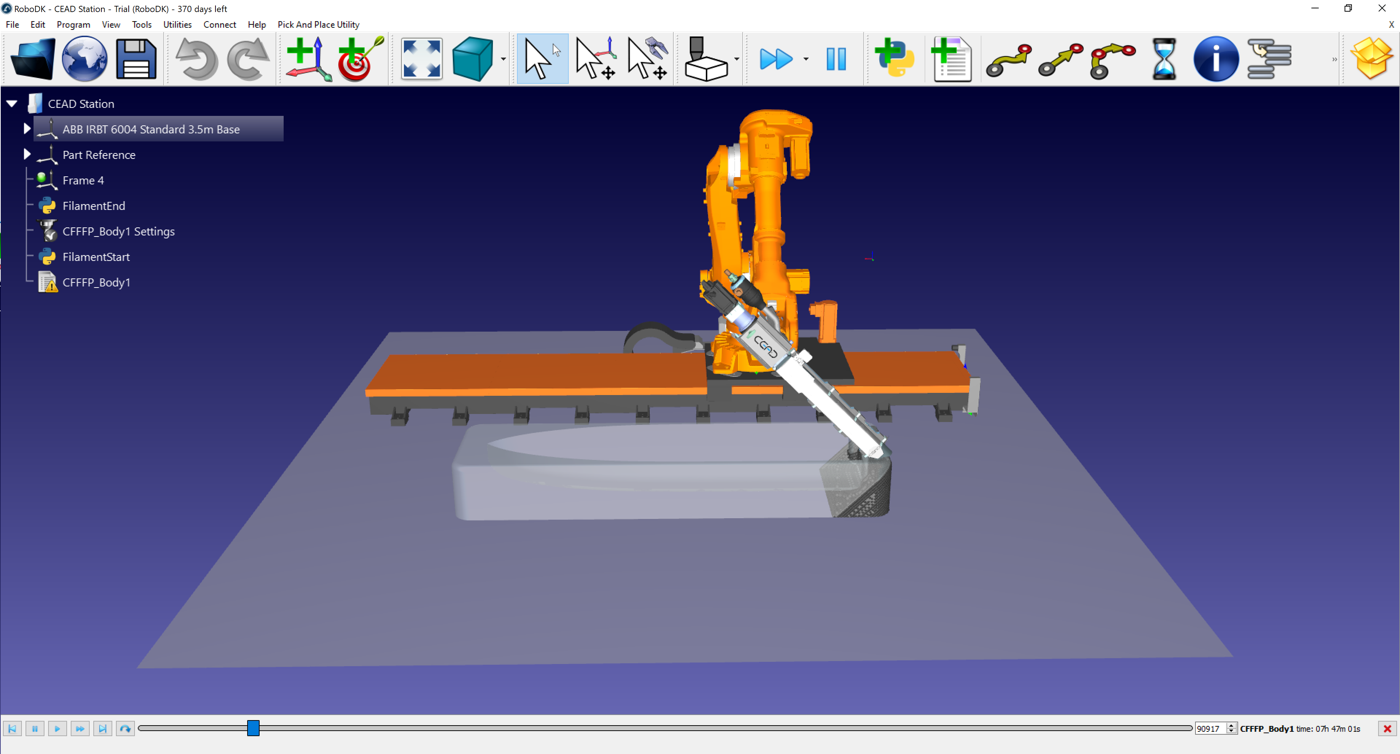
This example demonstrates how to use Cura with RoboDK for large-scale 3D printing of a boat hull mould using an ABB IRB 6640 robot, a CEAD extruder, and an ABB IRBT 6004 linear rail.
3D printing with Cura and RoboDK is possible in one of the following ways:
1.Create a Custom FFF Printer in Cura to match the robot’s workspace.
2.Import the 3D model (STL file) into Cura and apply a 45° tilt before slicing.
3.Slice the rotated STL and generate a G-code program.
4.Convert the Cura G-code to a robot program in RoboDK.
5.Simulate the tilted extrusion process in RoboDK and export ABB RAPID code.
Create a Custom Printer in Cura
Open Ultimaker Cura → Settings → Printer → Add Printer, then select Custom → Custom FFF Printer.
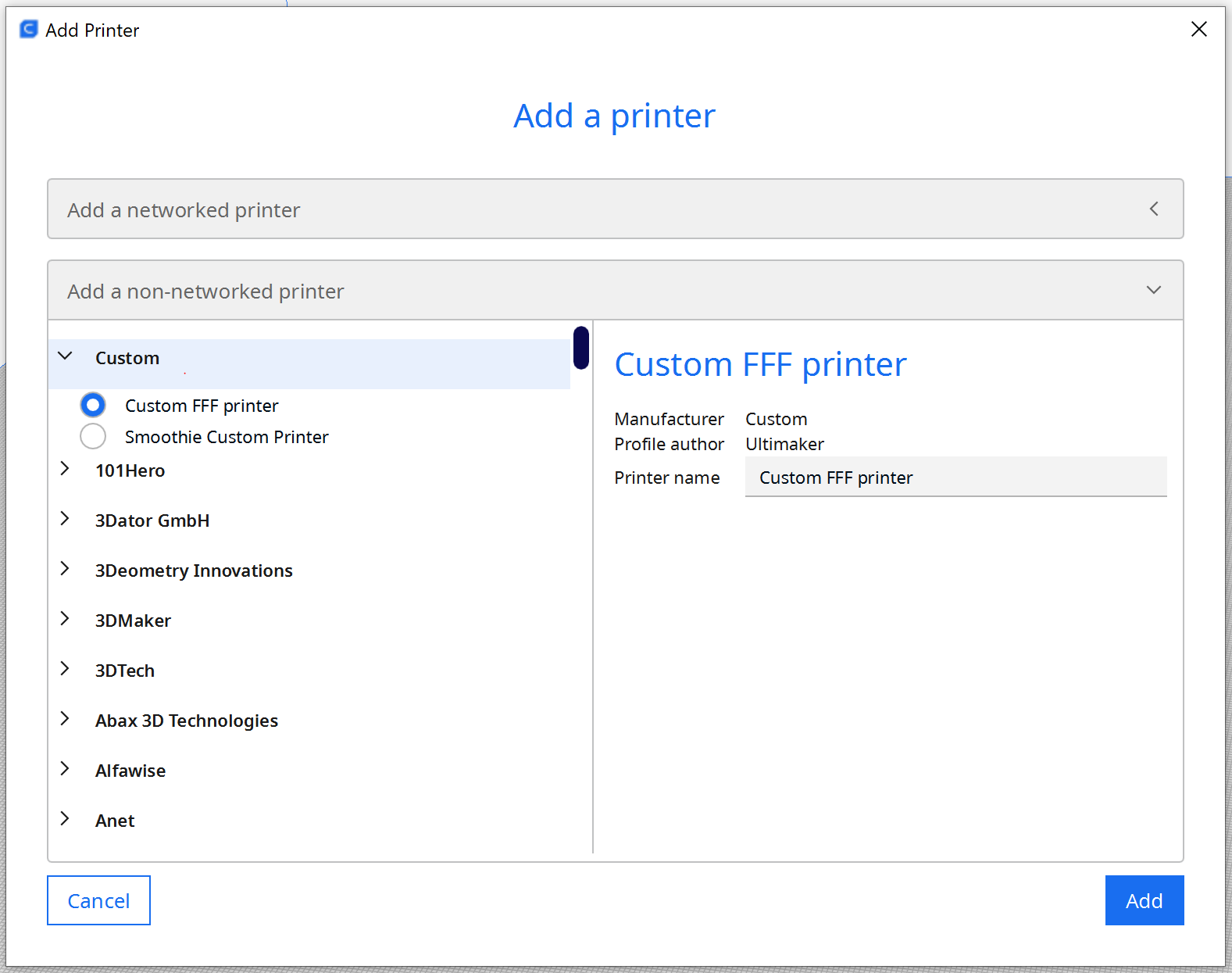
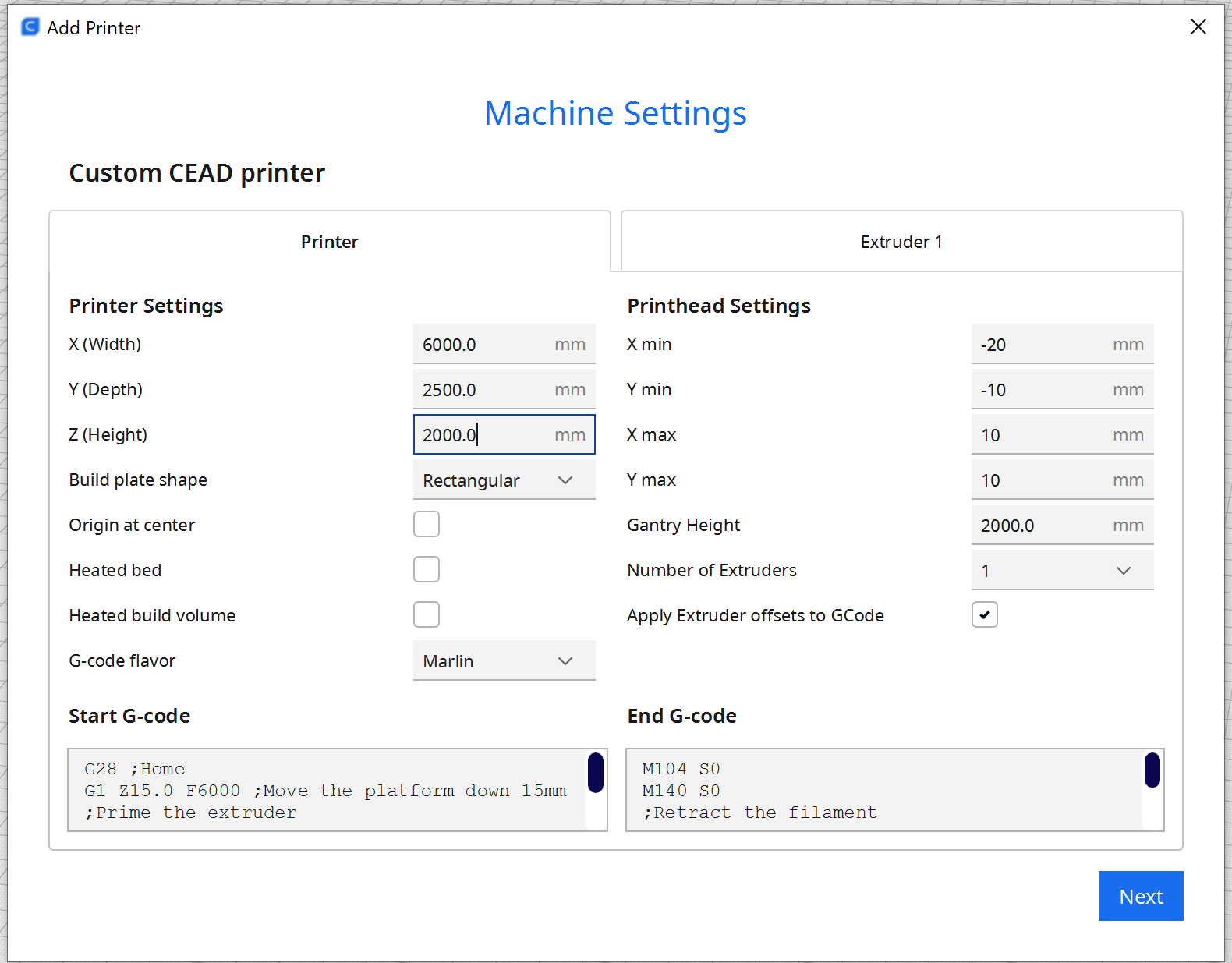
Set the build volume to match the robot and rail:
1.X: 6000 mm
2.Y: 2500 mm
3.Z: 2000 mm
Disable heater controls because the CEAD extruder manages heating externally.
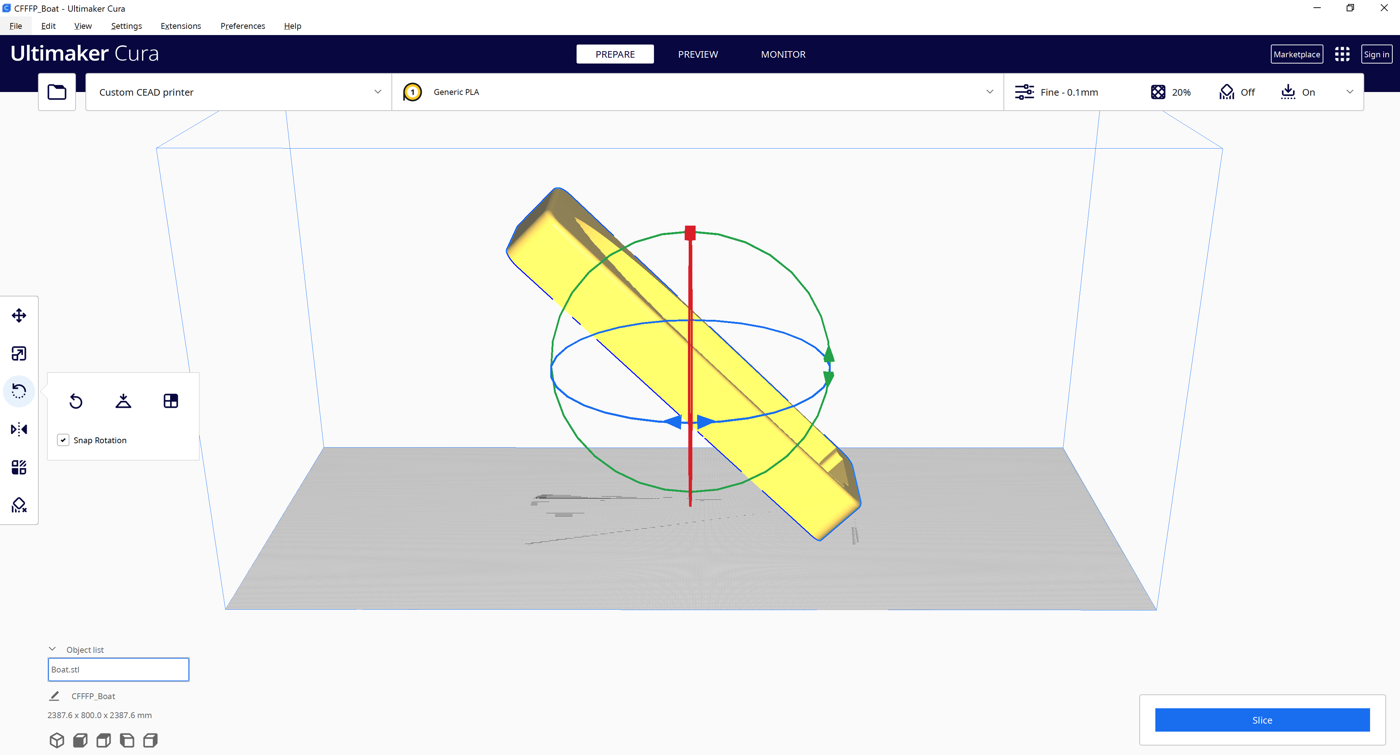
Apply a 45° Tilt in Cura
The STL model must be rotated 45° in Cura before slicing.
1.Select the object.
2.Use Cura’s Rotate tool to tilt the part 45°.
3.Slice the rotated STL.
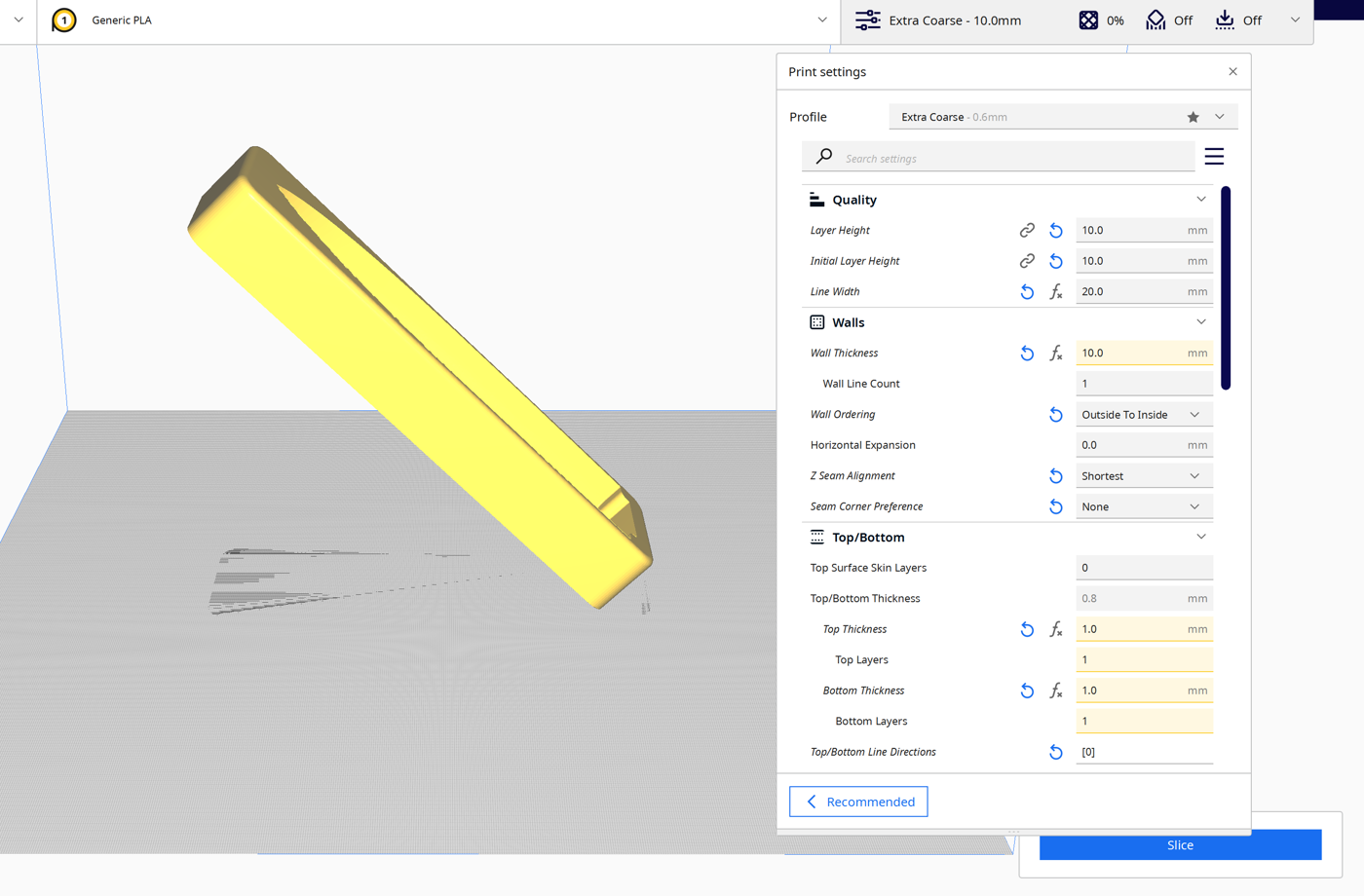
Generate and Import G-code
After tilting the model, slice it in Cura and save the program as a .gcode file.
In RoboDK, select Utilities → Convert NC Program and choose the Cura file.
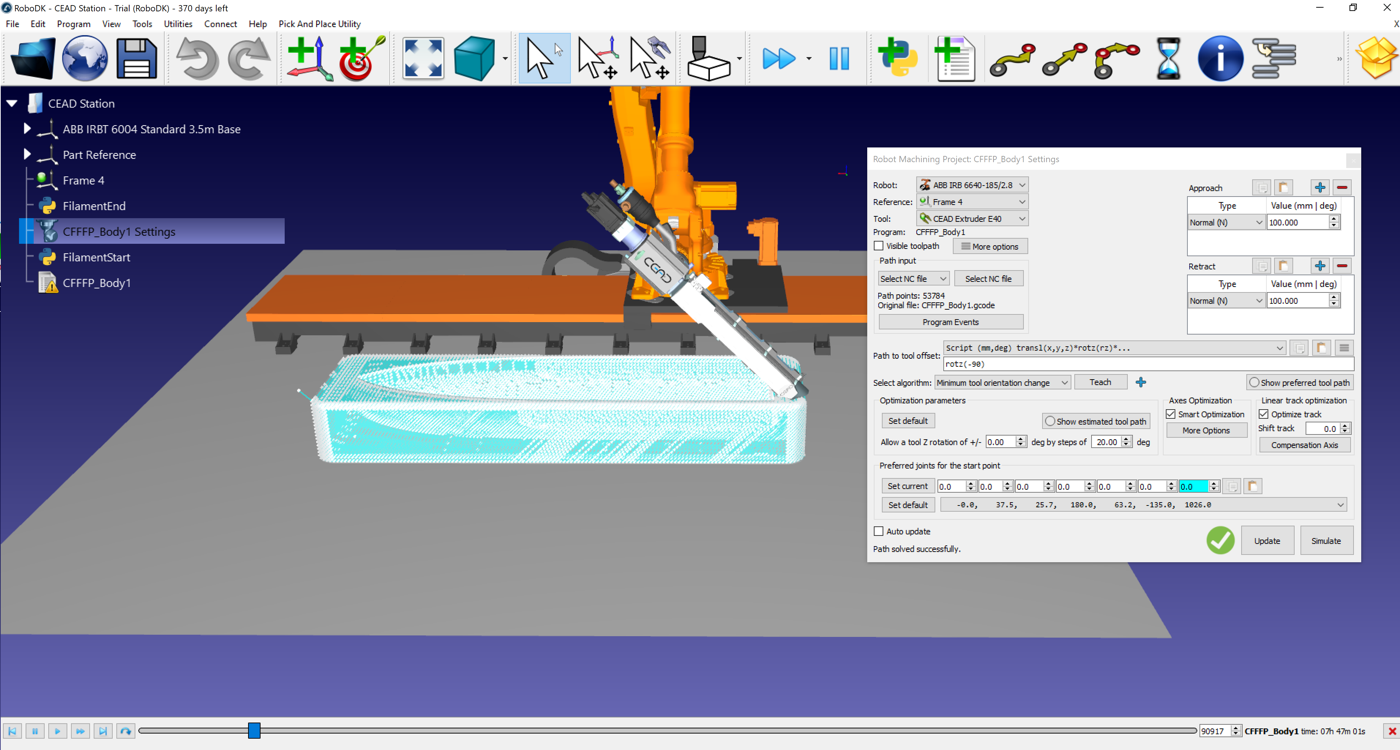
In the NC import dialog:
1.Select the ABB IRB 6640 robot.
2.Add the ABB IRBT 6004 rail as an external axis.
3.Select the CEAD extruder as the tool.
4.Define the reference frame (boat hull platform).
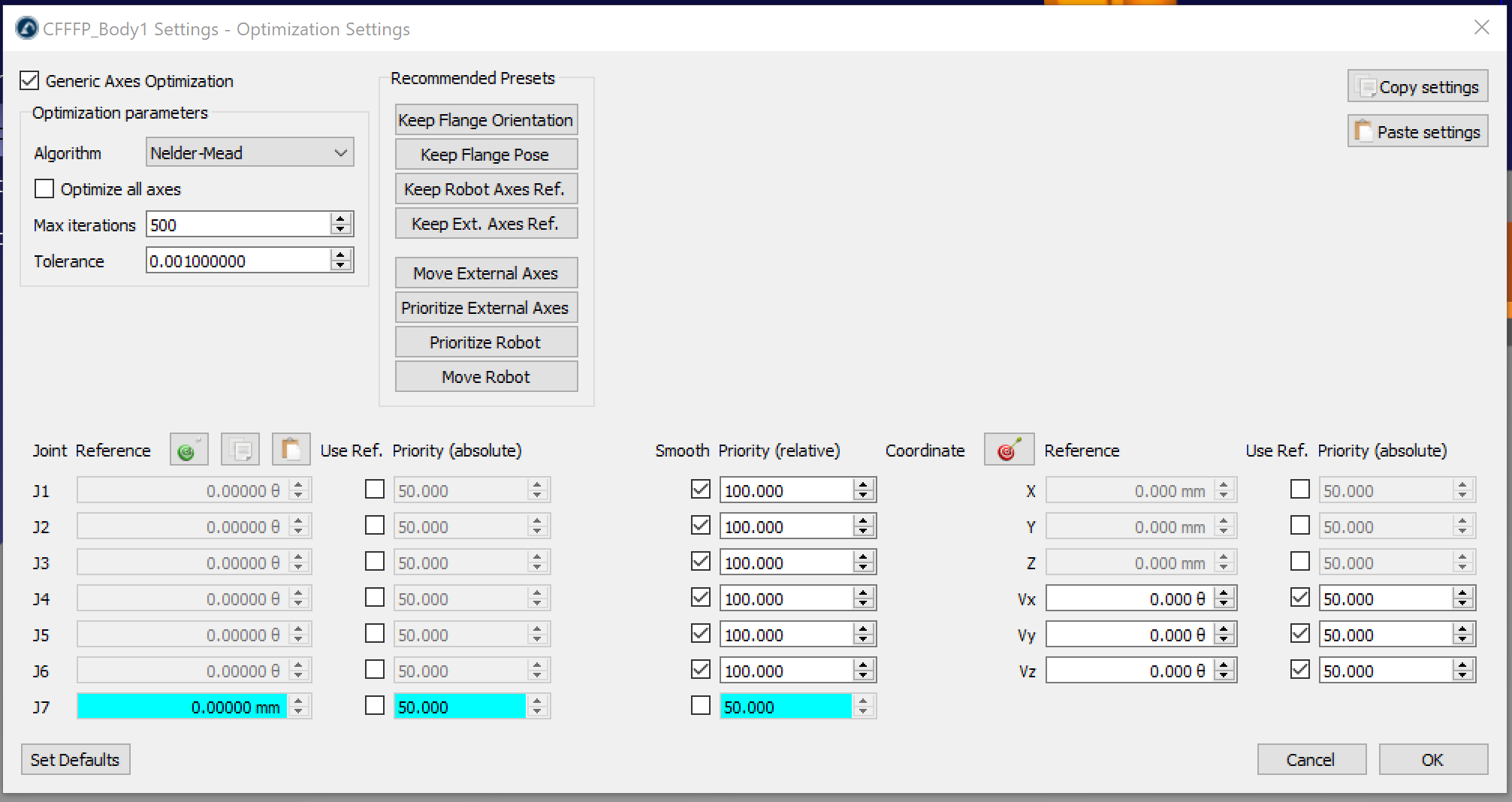
Extruder Synchronization
By default, RoboDK translates Cura’s E directive as a program call to a program called Extruder, passing the E value as a parameter.
This can be modified in Tools → Options → Program Events.
Simulation of 45° Printing
When the Cura G-code is imported, RoboDK simulates the tilted extrusion process:
1.The ABB IRB 6640 follows the Cura toolpath.
2.The CEAD extruder is synchronized with robot motion.
3.The tool orientation reflects the 45° tilt applied in Cura.